
Each of these tests has a relatively high false-positive rate (i.e., 50 percent) in the low-risk patient. In controlled trials, Doppler analysis has been associated with improved outcome, 1 although it is considered experimental by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The use of Doppler flow velocimetry, usually of the umbilical artery, identifies the growth-restricted fetus at greatest risk for neonatal morbidity and mortality. The biophysical profile involves assessment of fetal well-being with a combination of the nonstress test and four ultrasonographic parameters (amniotic fluid volume, respiratory movements, body movements and muscle tone). Options include the nonstress test, the biophysical profile and an oxytocin (Pitocin) challenge test.
In any case, antenatal testing should be instituted. Although not of proven benefit, bed rest may maximize uterine blood flow. General management measures include treatment of maternal disease, cessation of substance abuse, good nutrition and institution of bed rest. The fetus should be monitored continuously during labor to minimize fetal hypoxia. Preterm delivery is indicated if the fetus shows evidence of abnormal function on biophysical profile testing. General management measures include treatment of maternal disease, good nutrition and institution of bed rest. This content does not have an Arabic version. This content does not have an English version.
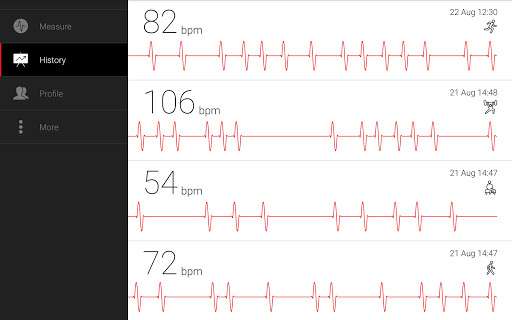
#Normal cardiograph serial
Serial ultrasonograms are important for monitoring growth restriction, and management must be individualized. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) - Mayo Clinic This common, painless test can detect heart attacks and heart rhythm problems. A lag in fundal height of 4 cm or more suggests IUGR. Growth restriction is classified as symmetric and asymmetric. Ultrasound biometry is the gold standard for assessment of fetal size and the amount of amniotic fluid. Accurate dating early in pregnancy is essential for a diagnosis of IUGR. Certain pregnancies are at high risk for growth restriction, although a substantial percentage of cases occur in the general obstetric population. Identification of IUGR is crucial because proper evaluation and management can result in a favorable outcome. The PR segment represents the electrical conduction through the atria and the delay of the electrical impulse in the atrioventricular node.Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is a common diagnosis in obstetrics and carries an increased risk of perinatal mortality and morbidity. This slowing signal appears as a flat line on the ECG between the end of the P wave and the beginning of the Q wave. The signal slows down as it passes through this node, allowing the ventricles to fill with blood. The electrical signal passes from the atria to the ventricles through the atrioventricular (AV) node (2). The PR Interval is the time, in seconds, from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex. This electrical signal is recorded as the P wave on the ECG. The electrical signal begins in the sinoatrial node (1) which is located in the right atrium and travels to the right and left atria, causing them to contract and pump blood into the ventricles.
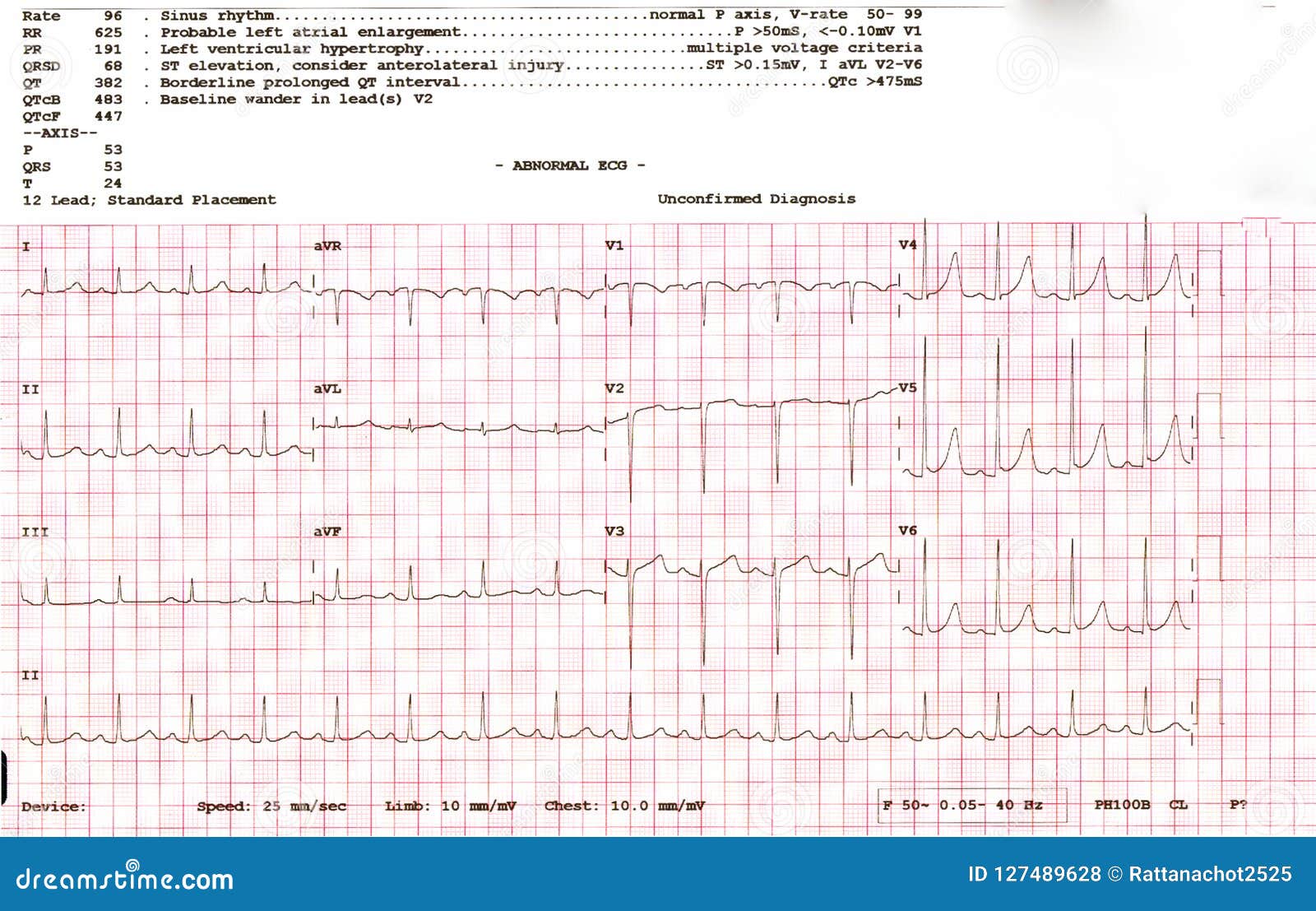
This information is recorded on a graph that shows each phase of the electrical signal as it travels through your heart. Also known as an electrocardiogram or an EKG, an ECG is a test that detects and records the strength and timing of the electrical activity in your heart.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
